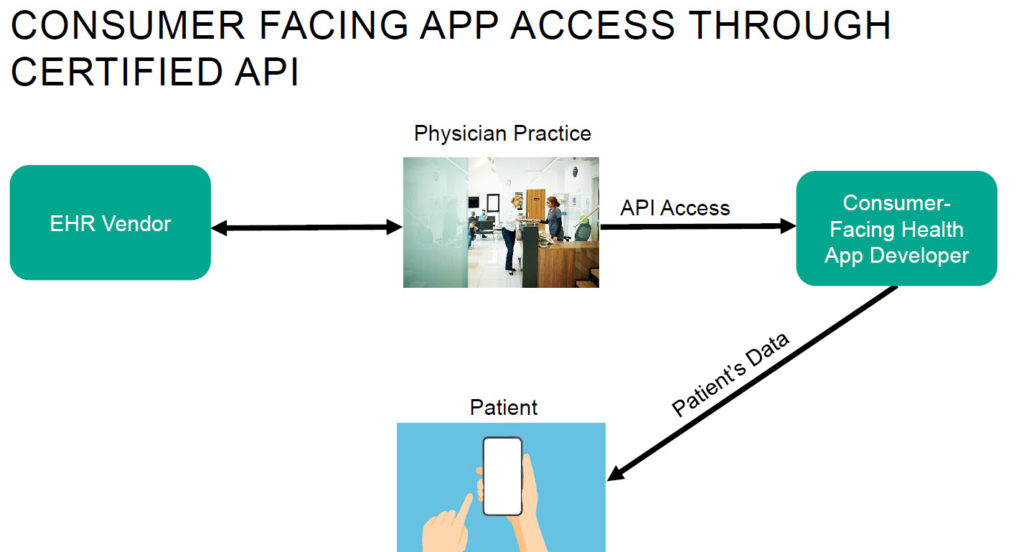
A bipartisan pair of US senators have proposed legislation that would allow certain controlled substances to be prescribed via an initial telehealth encounter and—under certain conditions—expand Medicare reimbursement of audio-only substance use disorder treatment services. The proposed TREATS Act has been referred to the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions, and could significantly reduce the regulatory burdens associated with the remote prescribing of controlled substances.
For more than a decade, healthcare providers in the United States have been largely prohibited from prescribing controlled substances via telehealth without having previously performed an in-person medical evaluation of the patient. Although Congress created the framework for a “special registration” pathway that has the potential to more broadly permit the practice, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) has not issued regulations to implement it. This has been a significant roadblock for the treatment of substance use disorder, which is often treated with controlled substances. Recently, Senators Rob Portman (R-OH) and Sheldon Whitehouse (D-RI) proposed the Telehealth Response for E-prescribing Addiction Therapy Services Act (the TREATS Act), which would allow certain controlled substances to be prescribed via telehealth. The TREATS Act also proposes to expand Medicare reimbursement of audio-only substance use disorder treatment services, if certain conditions are met. The TREATS Act was introduced on June 30, 2020, and has been referred to the Committee on Health, Education, Labor, and Pensions.
Remote Prescribing of Schedules III and IV Controlled Substances
The remote prescribing of controlled substances has been stymied by the Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008 (the Ryan Haight Act), which typically requires providers to perform an in-person medical evaluation of the patient prior to prescribing controlled substances. The Ryan Haight Act does incorporate seven pathways by which practitioners can prescribe controlled substances via telemedicine without a prior in-person examination, but these exceptions are extremely narrow and it is difficult for most providers to meet their requirements. One of the pathways, however, called for a “special registration process” that had the potential to more broadly permit providers to prescribe controlled substances via telemedicine. Congress left the implementation of the special registration process up to the DEA—and the DEA never issued regulations to implement it. After ten years of silence, Congress again pushed the DEA to act, imposing a second deadline for the DEA to implement regulations regarding the special registration process by October 24, 2019, under the SUPPORT for Patients and Communities Act. While there were rumblings that the DEA was prepared to act in late 2019, it is still yet to issue a proposed rule regarding the special registration process.
As we explained in a prior On the Subject, the COVID-19 public health emergency ushered in a significant, albeit temporary, change to the Ryan Haight Act, permitting providers to prescribe controlled substances via telehealth without a prior in-person medical evaluation during the pendency of the public health emergency declared [...]
Continue Reading
read more

 Subscribe
Subscribe